
Isopropyl alcohol is not active against the nonlipid enteroviruses but is fully active against the lipid viruses 72. Įthyl alcohol, at concentrations of 60%–80%, is a potent virucidal agent inactivating all of the lipophilic viruses (e.g., herpes, vaccinia, and influenza virus) and many hydrophilic viruses (e.g., adenovirus, enterovirus, rhinovirus, and rotaviruses but not hepatitis A virus (HAV) 58 or poliovirus) 49. Isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol) was slightly more bactericidal than ethyl alcohol for E. The gram-positive organisms Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes were slightly more resistant, being killed in 10 seconds by ethyl alcohol concentrations of 60%–95%. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was killed in 10 seconds by all concentrations of ethanol from 30% to 100% (v/v), and Serratia marcescens, E, coli and Salmonella typhosa were killed in 10 seconds by all concentrations of ethanol from 40% to 100%. The bactericidal activity of various concentrations of ethyl alcohol (ethanol) was examined against a variety of microorganisms in exposure periods ranging from 10 seconds to 1 hour 483. Methyl alcohol (methanol) has the weakest bactericidal action of the alcohols and thus seldom is used in healthcare 488. The bacteriostatic action was believed caused by inhibition of the production of metabolites essential for rapid cell division. Protein denaturation also is consistent with observations that alcohol destroys the dehydrogenases of Escherichia coli 486, and that ethyl alcohol increases the lag phase of Enterobacter aerogenes 487 and that the lag phase effect could be reversed by adding certain amino acids. This mechanism is supported by the observation that absolute ethyl alcohol, a dehydrating agent, is less bactericidal than mixtures of alcohol and water because proteins are denatured more quickly in the presence of water 484, 485. The most feasible explanation for the antimicrobial action of alcohol is denaturation of proteins. Their cidal activity drops sharply when diluted below 50% concentration, and the optimum bactericidal concentration is 60%–90% solutions in water (volume/volume) 483, 484.

These alcohols are rapidly bactericidal rather than bacteriostatic against vegetative forms of bacteria they also are tuberculocidal, fungicidal, and virucidal but do not destroy bacterial spores. FDA has not cleared any liquid chemical sterilant or high-level disinfectant with alcohol as the main active ingredient.
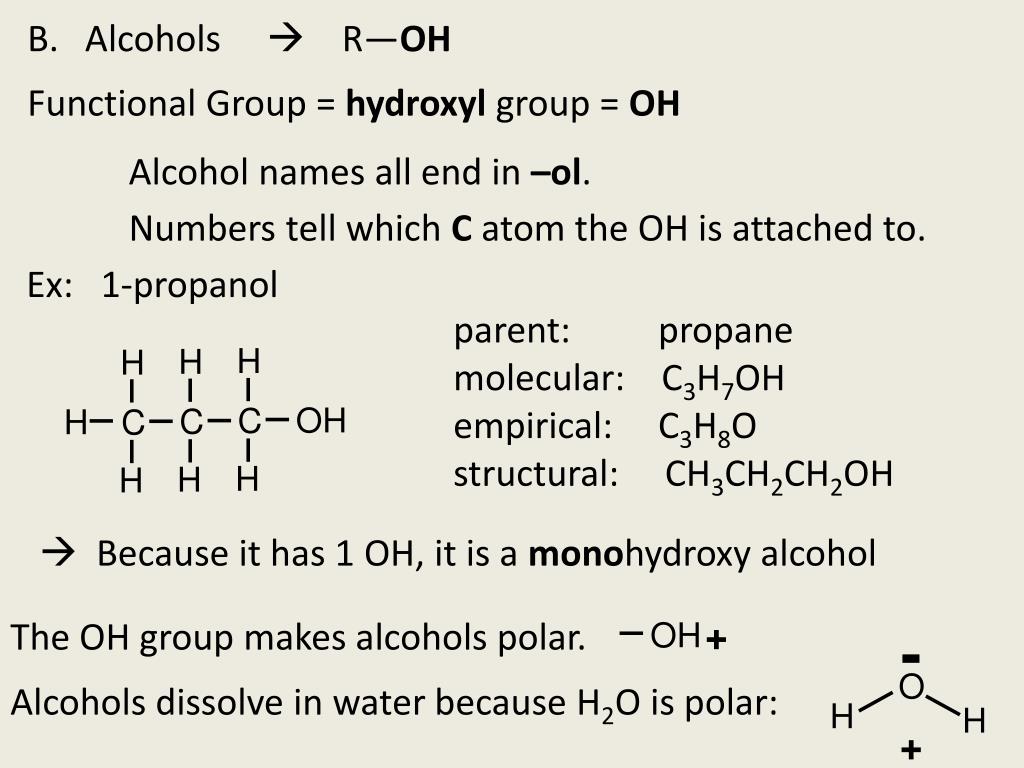
In the healthcare setting, “alcohol” refers to two water-soluble chemical compounds-ethyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol-that have generally underrated germicidal characteristics 482.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
